Burn Awareness Month, every February, focuses on raising public awareness about burn hazards, their prevention, and the significance of safety protocols. This initiative aims to educate individuals on various types of burns and the measures needed to avoid them. It emphasizes the importance of proper safety practices to reduce burn incidents.
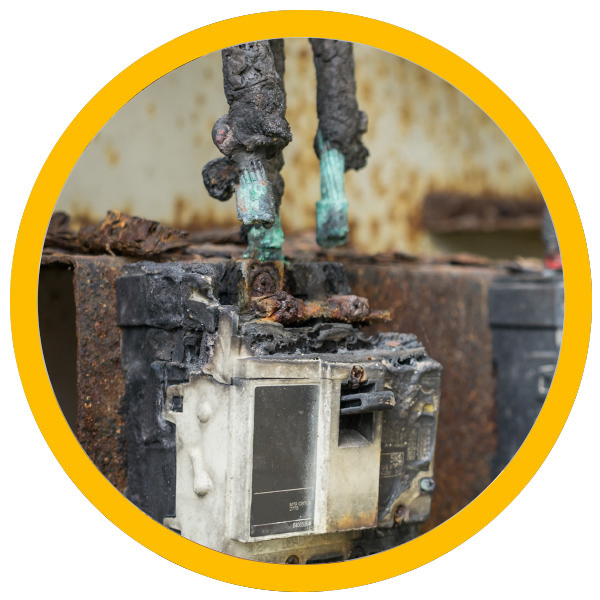
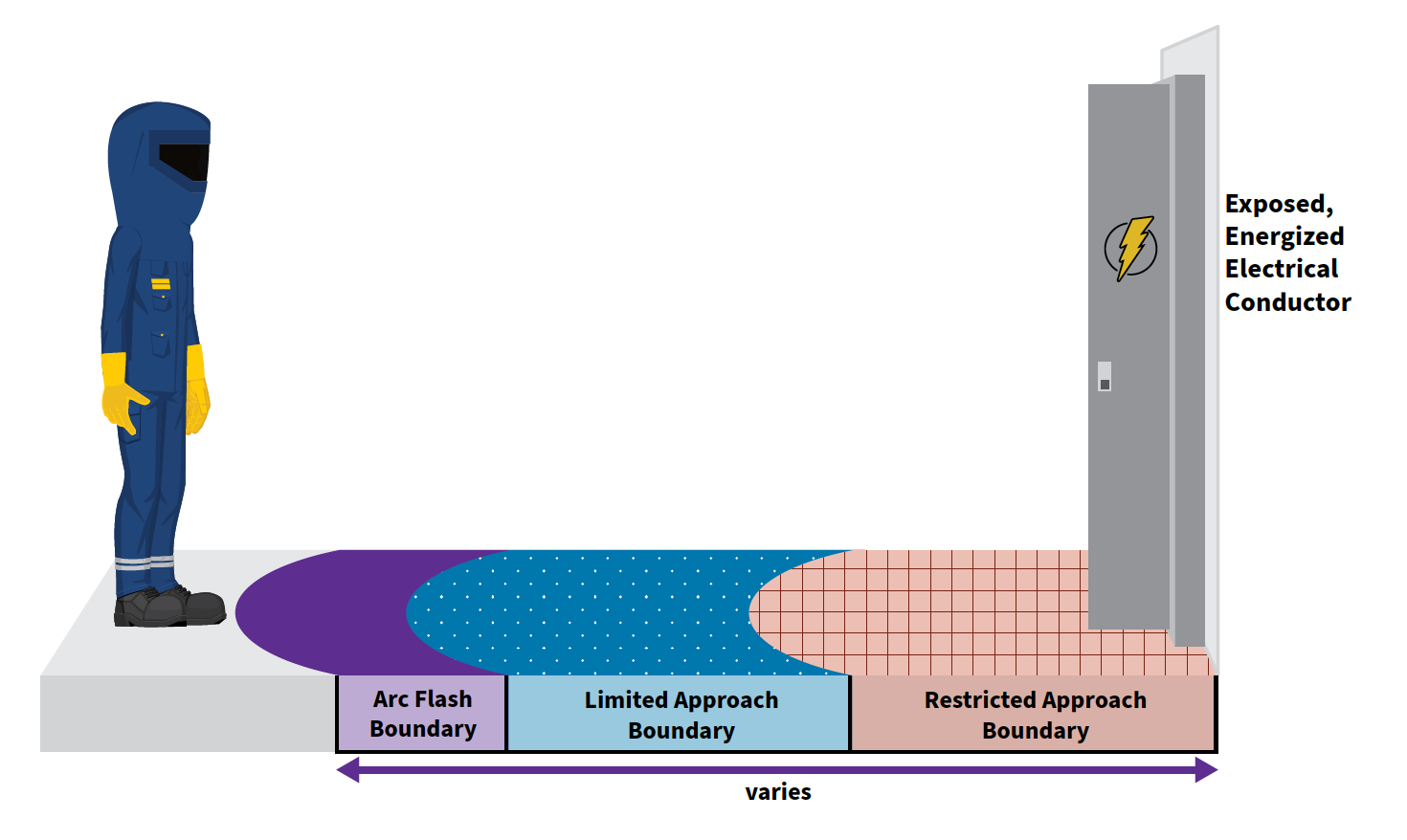
Burn hazards are particularly prevalent in industrial settings, where risks such as arc flashes pose serious threats to worker safety. These incidents highlight the necessity for comprehensive safety programs and effective preventive measures. Employers and employees must be well-informed about these dangers of burns and the steps they can take to mitigate risks.
Public awareness campaigns during Burn Awareness Month provide a platform for sharing critical burn prevention information through training sessions, educational materials, and safety audits to maintain compliance with safety standards. This proactive approach helps in identifying potential hazards and addressing them before they result in injuries.
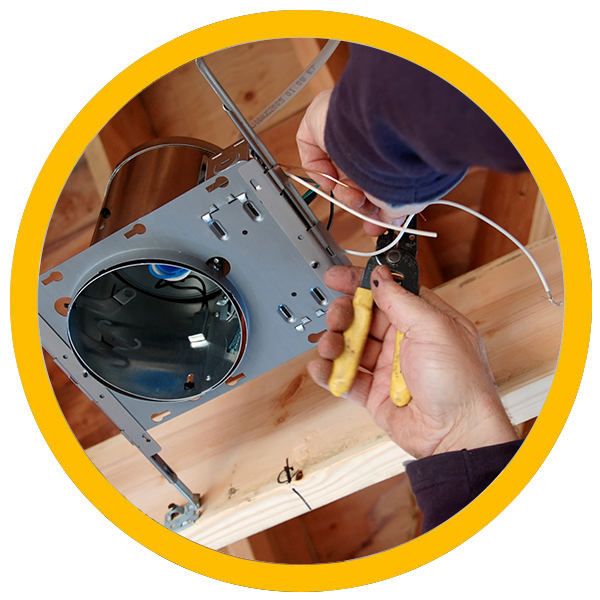
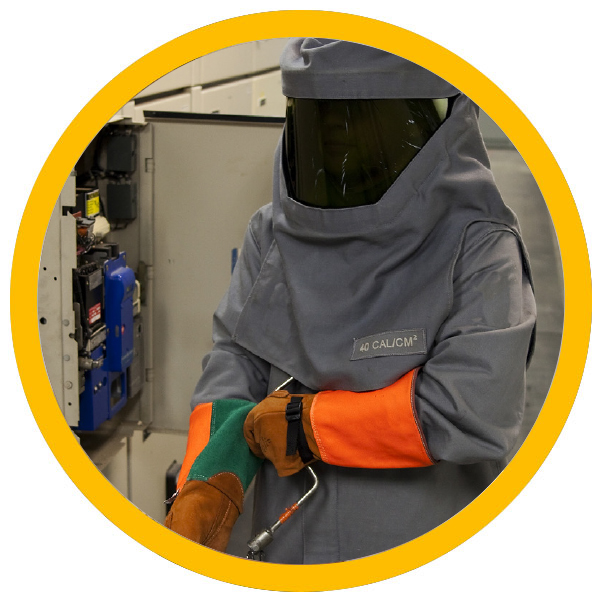
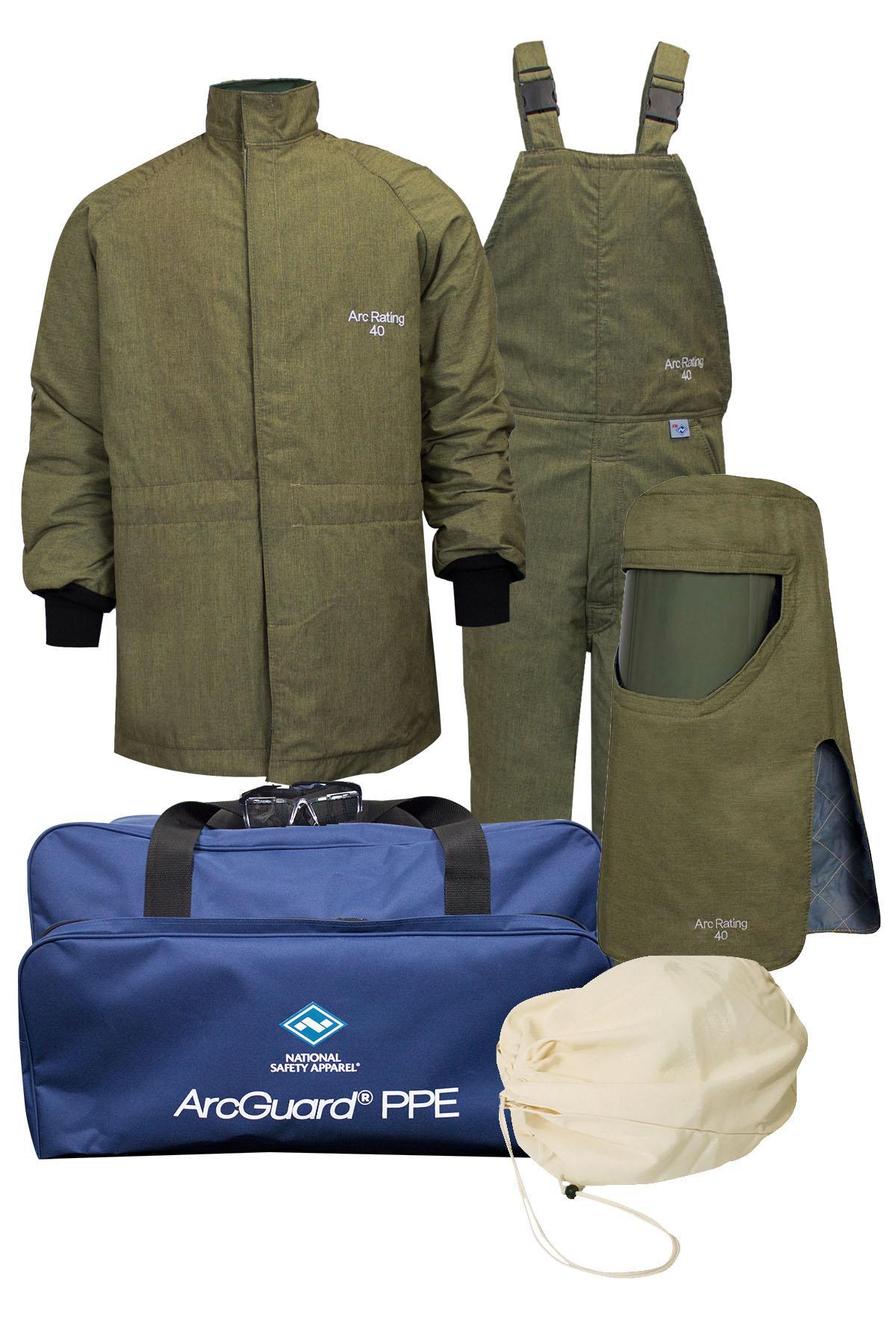
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is an essential component in preventing burn injuries. By ensuring that workers have access to the right PPE and understand how to use it correctly, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of burn incidents. Additionally, routine maintenance and regular safety checks of equipment are crucial in preventing malfunctions that could lead to arc flashes and other burn hazards.
Burn Awareness Month highlights the importance of staying cautious and informed to prevent burn injuries. When safety measures and best practices are followed, workplaces become safer for everyone.