With global temperatures on the rise, it’s important to understand what heat stress is and how to protect yourself and your co-workers from its effects.
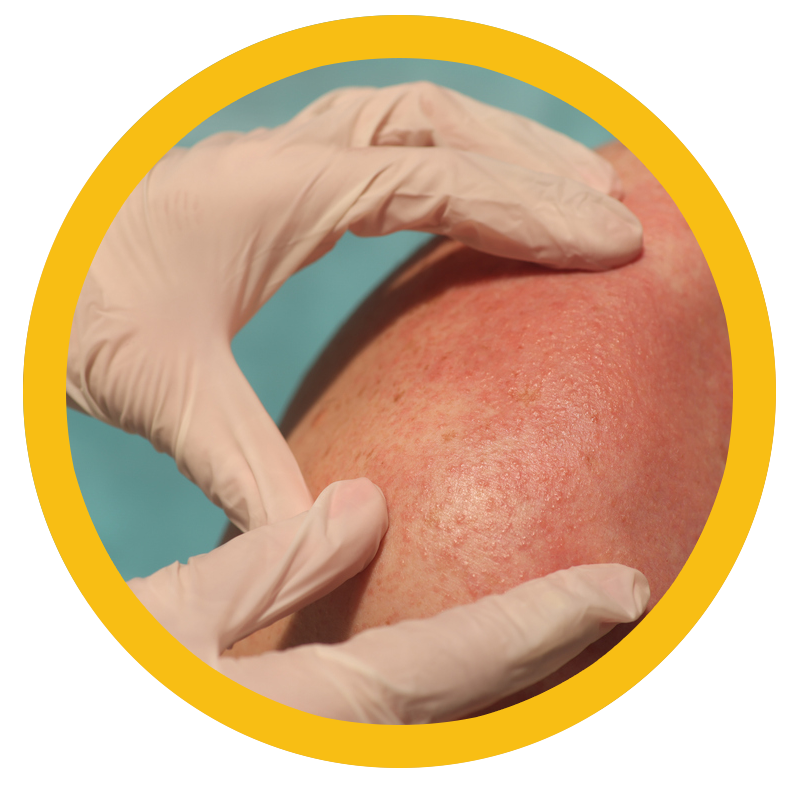
Heat stress is the combination of environmental heat, physical activity, and clothing worn, which can cause an individual to become overheated and experience symptoms of heat illness.
Heat illness can range from heat cramps and heat exhaustion to the most serious, heat stroke. Heat-related illnesses occur when a person’s body is unable to cool itself properly and can lead to serious health problems and even death. The most common signs and symptoms of heat stress are excessive thirst, headache, dizziness, nausea, and fatigue.
Employers need to understand the risks of working in hot environments and take steps to reduce the risk of heat stress from occurring.
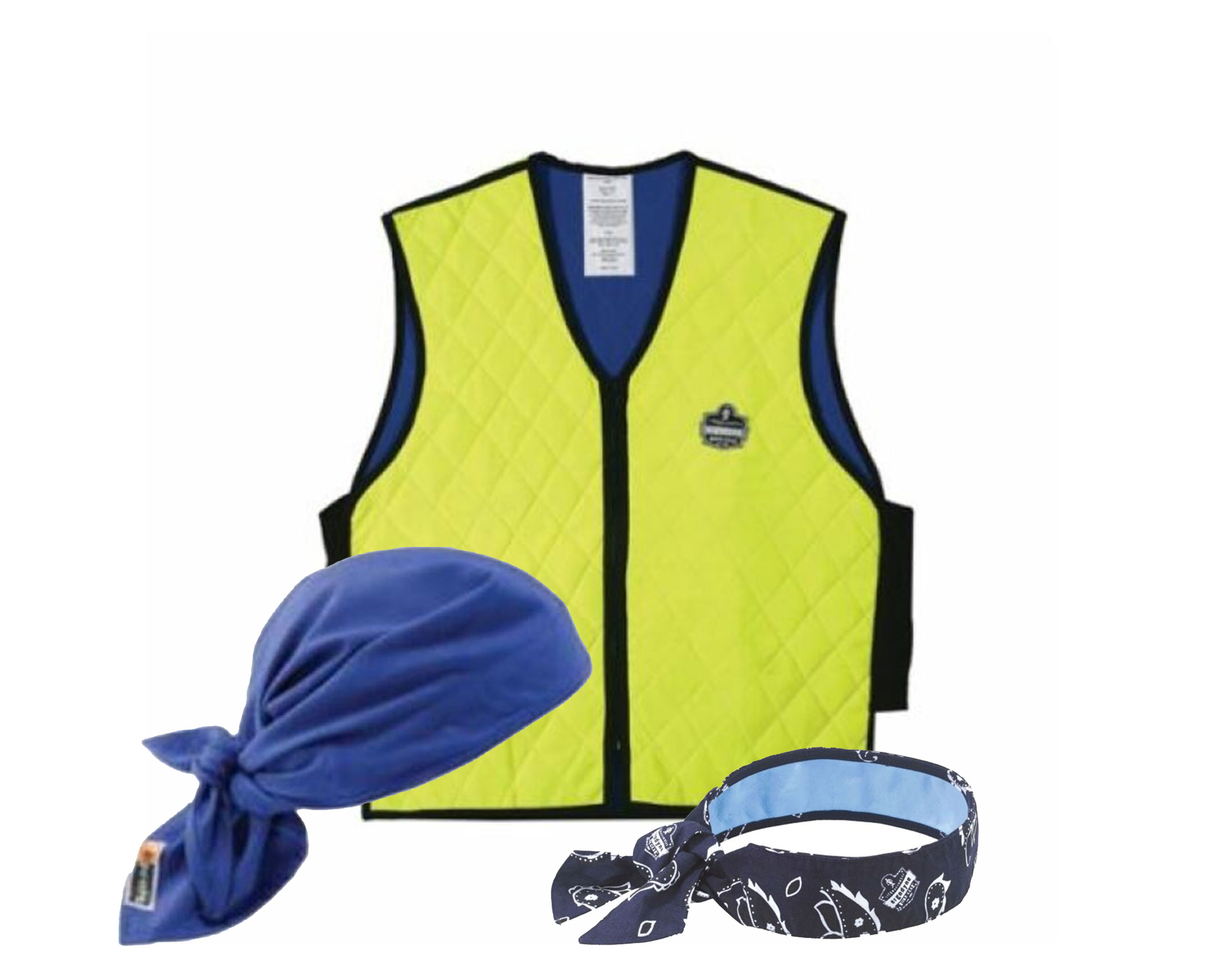
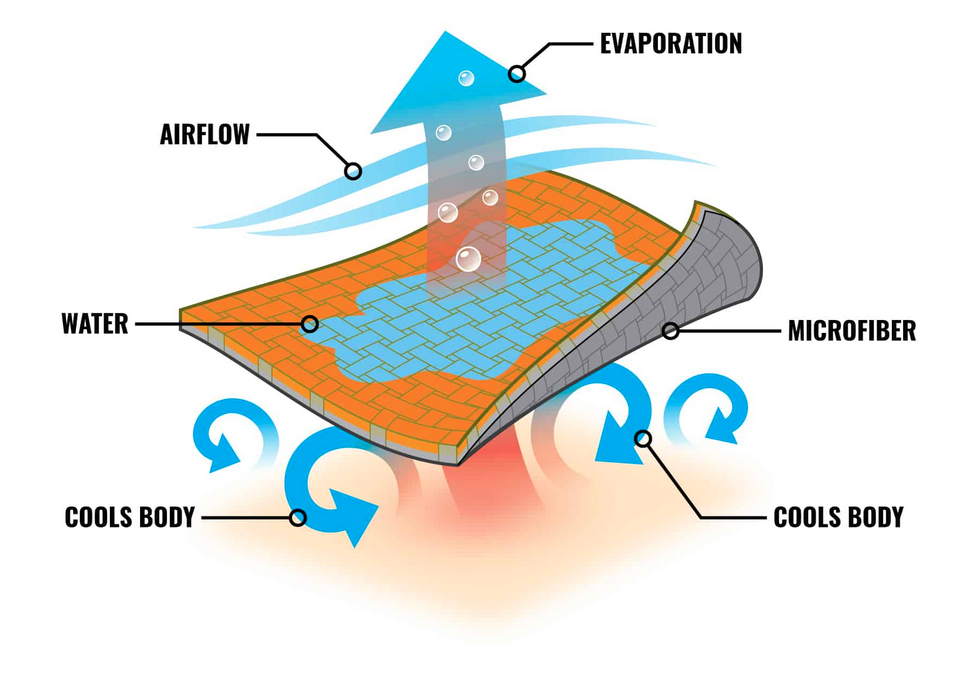
Employers can provide their workforce appropriate cooling materials like vests and apparel, such as cooling hats, cooling towels, and moisture-wicking clothing. It’s important that workers have access to cool, clean drinking water that is cooler than ambient air as well as electrolytes to help them stay hydrated. Developing a hydration program to guide employees on best use practices and how to incorporate hydration into their breaks and shift lengths will provide an immediate impact and help avoid over-exertion. Ideally break locations are indoors or under a shaded area.